
Extracting Bromine from sea water
- Bromine is used in a variety of ways:
- In flame retardants
- In bromomethane, a chemical used as a fumigant against pests.
- It used to be used as an anti-knock substance with lead, but this has been phased out as lead compounds damage the environment, and catalytic converters.
Manufacturing Bromine
- The manufacturing process of bromine involves four main stages:
- Oxidation of bromide ions into bromine.
- Bromine vapour removal.
- Hydrogen bromide production.
- Oxidation of hydrogen bromide to bromine.
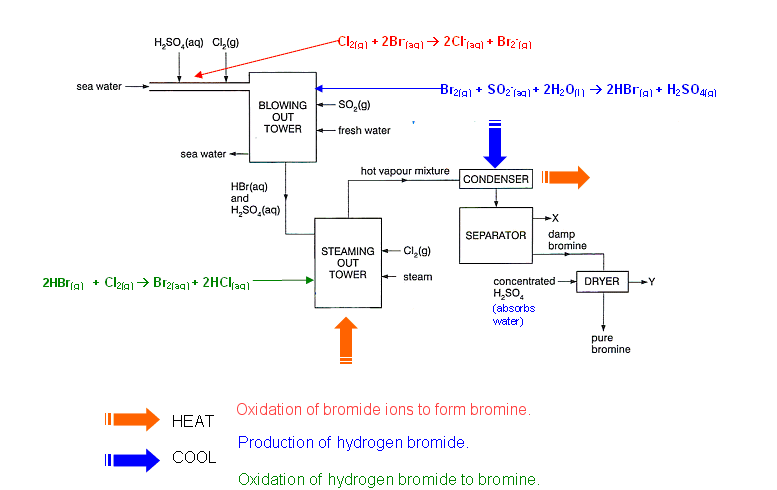
Oxidation of bromide ions to form bromine
- Sea water contains approximately 65,000 tonnes of bromine. This bromine is removed from the sea water by displacement of the bromide ions using chlorine:
Cl2(g) + 2Br-
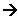 2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)
2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)
- The acidity is adjusted to pH 3.5 to prevent hydrolysis of the liberated bromine and chlorine:
Bromine vapour removal
- Bromine mixture is air blown, by large fans, through the reaction mixture.
Production of hydrogen bromide
- A fine mist of sulphur dioxide and water are mixed with the bromine vapour.
- The hydrogen bromide and sulphuric acid mist formed are removed from the air by passing the mist through a layer of glass fibre, causing the acids to condense.
- The bromine at this stage is 2200 times more concentrated than it is in sea water.
Oxidation of hydrogen bromide to bromine
- The acid is oxidised with chlorine to liberate bromine:
2HBr(g) + Cl2(g)
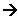 Br2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
Br2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
- This is achieved by feeding the hydrogen bromide into the top of a tower to meet a counter-current stream of steam and chlorine.
- The bromine vapour is removed from the mixture by steam distillation.
- The hot vapour mixture is condensed to form an aqueous layer of bromine, which is then dried using concentrated sulphuric acid.
How a Hazardous chemical like Bromine is handled
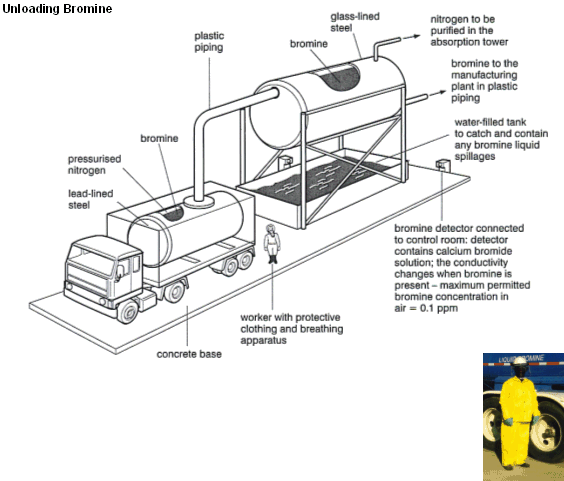
- Bromine is an extremely nasty substance. Bromine has a dark and dense choking vapour (its name comes from the Greek Bromos which translates to “Stench”).
- Due to its unsavoury properties, bromine has to be handled very carefully.
- When working with bromine protective suits must be warn, with special breathing apparatus (right).
- Bromine storage tanks are lined with glass, which is hard to corrode and allows the bromine to be visible.
- The tanks have bromine detectors that can sense when concentrations rise above the permitted 0.1 ppm.
Useful books for revision:
Revise AS Chemistry for Salters (Written by experienced examiners and teachers of Salter's chemistry)
Revise AS Chemistry for Salters (OCR) (Salters Advanced Chemistry)
Home
 2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)
2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)
 2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)
2Cl-(aq) + Br2(g)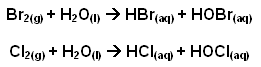
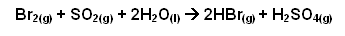
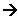 Br2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
Br2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
